Summary:
Insurance claims automation uses AI to streamline the claims lifecycle from FNOL to settlement by reducing manual work, improving accuracy, and speeding up claim decisions. This guide explains how AI enhances claims processing, where human oversight remains important, and what insurers should evaluate when selecting an automation vendor. It also highlights key factors like scalability, compliance, and integration to ensure insurers adopt solutions that deliver long-term operational value.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, insurance claims automation isn’t just a trend; it’s a must-have. Insurers are increasingly adopting AI to not only streamline their claims processes but also to reduce costs and enhance customer experiences. Yet, many companies find themselves facing hurdles when trying to implement AI effectively and achieve real results. This guide aims to simplify the journey into the world of insurance claims automation and offers tips on how to evaluate potential vendor partners.
Why Insurance Claims Automation Often Fails to Deliver
Despite pouring resources into technology, many insurers discover that their automation efforts miss the mark. Here are some common stumbling blocks:
- Lack of clarity: Often, insurers dive into AI implementation with little understanding of their current processes, leading to outcomes that don’t quite connect.
- Short-term perspectives: Vendor choices are often made without a focus on long-term goals, creating gaps between expectations and capabilities.
- Integration challenges: Legacy systems can be a real roadblock, complicating effective AI integration and slowing down the benefits of automation.
- Choosing the right partner: The success of AI initiatives heavily depends on selecting the right technology partner, making this choice pivotal.
By avoiding these pitfalls, you can unlock the potential of AI to truly transform your claims processing.
Understanding the Role of AI in Modern Claims Handling
Insurance claims automation uses artificial intelligence to streamline and support different stages of the claims process. Instead of relying heavily on manual reviews, AI helps insurers capture, analyze, and process claim information more efficiently from First Notice of Loss (FNOL) to final settlement.
AI in Insurance enhances the claims journey by automatically extracting data from documents, identifying missing information, flagging potential fraud risks, and helping prioritize claims based on complexity. This allows insurers to handle routine claims faster while improving overall accuracy.
Unlike rule-based automation, which follows fixed instructions, AI-driven systems learn from data patterns and adapt over time. This enables smarter decision-making and more flexible claim handling.
However, human expertise remains essential. Claims adjusters still review complex cases, make judgment-based decisions, and ensure fair outcomes.
As claim volumes increase and customer expectations rise, many insurers are shifting toward AI automation to improve efficiency, reduce processing time, and deliver better policyholder experiences.
Where AI Creates Real Operational Impact in Claims
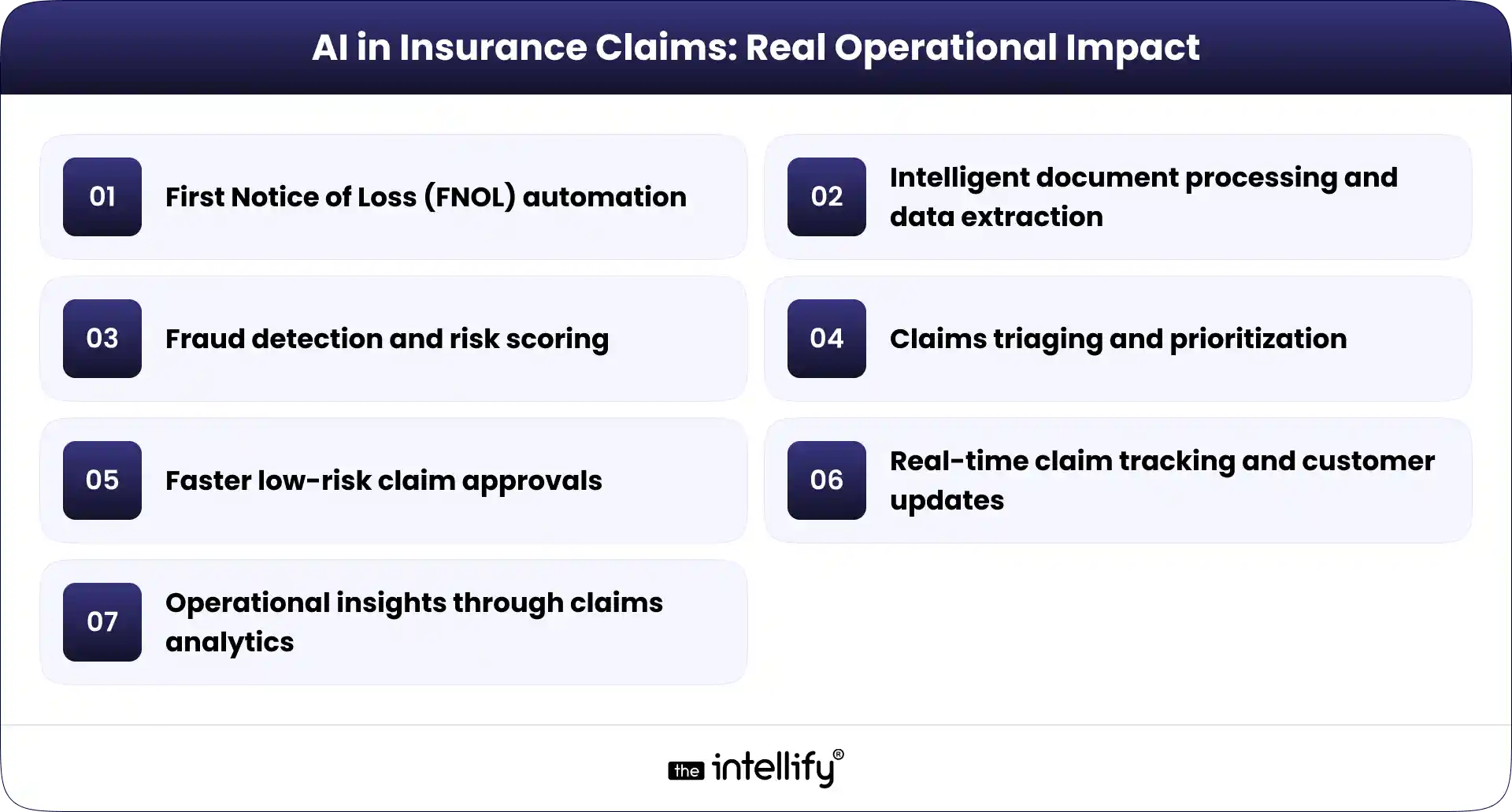
Artificial Intelligence goes beyond just automation; it enhances overall operational effectiveness. Here’s how AI can truly make a difference in various stages of claims handling:
- First Notice of Loss (FNOL) automation: Accurately and quickly capture claims data right from the start.
- Intelligent document processing and data extraction: Streamline data extraction from various document types, cutting down on manual tasks.
- Fraud detection and risk scoring: Use algorithms to efficiently spot potentially fraudulent claims.
- Claims triaging and prioritization: Speed up processing by categorizing claims based on complexity and risk factors.
- Faster low-risk claim approvals: Expedite straightforward claims, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Real-time claim tracking and customer updates: Keep customers informed throughout the claims journey with instant updates.
- Operational insights through claims analytics: Leverage analytics to derive meaningful insights that can improve processes.
Focusing on these areas gives insurers a solid edge in the market.
Understanding Your Current Claims Workflow Before AI Automation
Before jumping headfirst into automation, it’s essential to take a good look at your current claims workflow:
1. Gap Identification:- Pinpoint areas where the current process might be falling short, whether in speed, cost efficiency, or customer experience (CX).
2. Business objectives:- Clearly define what you want to achieve with automation—quicker claims, reduced fraud, improved customer interactions, etc.
3. IT Systems Assessment:- Review your existing technology stack and its readiness for integration.
4. Volume and Scalability:- Consider anticipated claims volume to ensure your automated processes can scale effectively.
5. Team alignment:- It’s vital for operations, compliance, and IT departments to work in harmony.
6. Setting realistic Expectations:- Be upfront about timelines and outcomes before diving in.
Having a strong grasp of your existing workflow will set you up for a smooth AI transition.
Structuring an Effective AI-Driven Claims Automation Model
To truly harness the power of AI in claims automation, focus on these core elements:
Industry Experience in Insurance Claims
A proven track record with insurers ensures a solid understanding of the complexities involved.
AI Capability and Practical Performance
Look for high accuracy in both document processing and fraud detection.
Integration and Technical Flexibility
Ensure compatibility with existing systems and check for robust API availability.
Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
Confirm that any vendor follows stringent data protection standards and regulatory guidelines.
Customization and Scalability
The solution should be adaptable to various claim types and scalable for volume increases.
Implementation and Ongoing Support
Look for a clear onboarding process along with continuous support for optimization.
Choosing a vendor that ticks these boxes can make a noticeable difference in your automation journey.
Evaluation Gaps in Insurance Claims Automation
As you assess potential vendors, keep an eye on these common pitfalls that could derail your selection process:
- Testing with real data: Evaluating AI without actual claims data can lead to misguided expectations.
- Long-term scalability: Many forget to consider scalability for future implementations.
- Integration Complexity: Not weighing integration challenges can set timelines back significantly.
- Explainability in AI: Overlooking the need for AI decisions’ transparency can lead to compliance headaches.
- Insurance-specific expertise: Assess vendors on their specialized knowledge within the insurance sector.
- Long-term vs. upfront cost: Prioritize overall value rather than just initial costs.
Measuring Business Impact After AI Automation
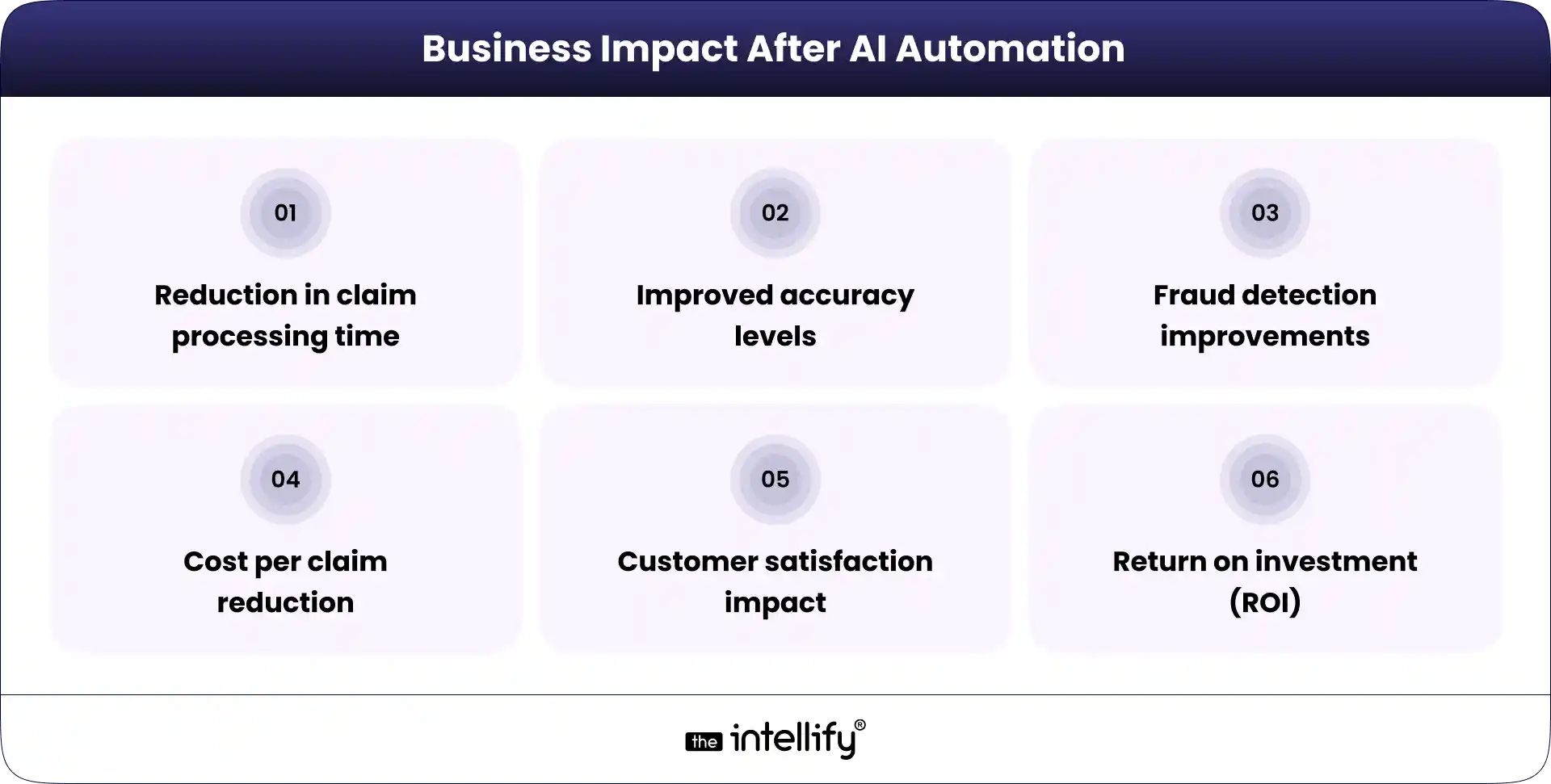
After implementing AI in claims processing, insurers need clear metrics to evaluate whether automation is delivering real operational value. Tracking measurable outcomes helps organizations understand how AI is improving efficiency, accuracy, and customer experience.
Some key performance indicators insurers typically monitor include:
1. Reduction in claim processing time: Faster turnaround times indicate improved operational efficiency and quicker settlements for policyholders.
2. Improved accuracy levels: Automation helps reduce manual errors in document review, data entry, and claim evaluation.
3. Fraud detection improvements: AI systems can identify suspicious patterns and flag high-risk claims earlier in the process.
4. Cost per claim reduction: Automating repetitive tasks can significantly lower operational costs over time.
5. Customer satisfaction impact: Faster resolutions and better communication can improve the overall claims experience.
6. Return on investment (ROI): Measuring financial returns against automation investments helps insurers assess long-term value.
Finding the Right Partner to Scale AI Claims Automation
Implementing AI in Insurance claims processing is not a one-time deployment. Long-term success depends on working with a partner who can support insurers as workflows evolve and automation expands across the claims lifecycle.
Why Vendor Partnership Matters
AI-driven claims automation requires continuous monitoring, optimization, and updates to maintain accuracy and efficiency as claim volumes and processes change.
Continuous Improvement
Automation systems improve over time through model refinement, performance monitoring, and workflow adjustments, helping insurers maintain operational efficiency.
Adapting to Regulatory Changes
Insurance regulations and compliance standards evolve regularly. Automation solutions must remain flexible to adapt to new regulatory and data protection requirements.
Working with Experienced Specialists
Collaborating with experienced AI specialists like The Intellify, who understand insurance workflows and claims automation, helps insurers implement scalable solutions aligned with real operational needs.
The Future of Insurance Claims Automation
The insurance industry is rapidly evolving, and AI will continue to play a major role in transforming how claims are processed. As automation technologies mature, insurers can expect faster decisions, better risk detection, and improved customer experiences.
Several trends are shaping the future of insurance claims automation:
- Predictive and proactive claims handling: AI will help insurers identify potential risks and claim patterns earlier, allowing faster and more informed decisions.
- Self-service claim experiences: Policyholders will increasingly be able to submit, track, and manage claims through AI-powered digital platforms.
- AI-assisted human decision-making: AI will support claims adjusters with insights and recommendations while humans handle complex judgment-based cases.
Continuous learning systems: AI models will keep improving as they process more data, enabling smarter and more efficient claims management over time.
Conclusion: Building a Smarter Claims Operation
Insurance claims automation is not just a technology upgrade, it’s a strategic step toward faster, more efficient claims operations. The success of automation largely depends on how carefully insurers evaluate their technology partners.
Focusing on capability, scalability, compliance, and long-term partnership helps ensure the solution can support evolving business needs. By taking a structured and well-informed approach, insurers can implement AI automation that delivers lasting operational value and better customer experiences.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
1. How does AI actually improve the insurance claims process?
AI helps reduce manual review work by automatically reading claim documents, detecting missing information, flagging potential fraud, and speeding up approvals. Instead of handling every step manually, teams can focus on complex cases while routine claims move faster.
2. What is insurance claims automation, and how is it different from basic workflow automation?
Insurance claims automation uses AI to make decisions and learn from data, not just follow fixed rules. Basic automation moves files from one step to another. AI-powered automation can analyze documents, assess risks, and support smarter claim handling.
3. Which parts of the claims lifecycle can be automated using AI?
AI can support First Notice of Loss (FNOL), document verification, fraud detection, claim triaging, approval recommendations, and even customer communication updates. It works best when applied to repetitive and data-heavy steps.
4. Is AI-based claims automation suitable for small and mid-sized insurers?
Yes. It doesn’t require a full system overhaul. Many insurers start by automating one area, such as document processing or fraud checks, and expand gradually. Scalability depends more on planning than on company size.
5. What should insurers evaluate before adopting AI for claims automation?
Insurers should assess their current workflow gaps, data quality, integration readiness, compliance requirements, and scalability goals. Clear objectives help ensure automation delivers measurable results.
6. How does AI help reduce fraud in insurance claims?
AI models analyze patterns across past claims to detect unusual behavior, duplicate submissions, or suspicious trends. This allows insurers to flag high-risk claims early without slowing down legitimate ones.
7. What kind of ROI can insurers expect from AI-driven claims automation?
Most insurers see improvements in claim turnaround time, operational efficiency, error reduction, and fraud savings. ROI depends on claim volume and automation scope, but often becomes visible within the first year.